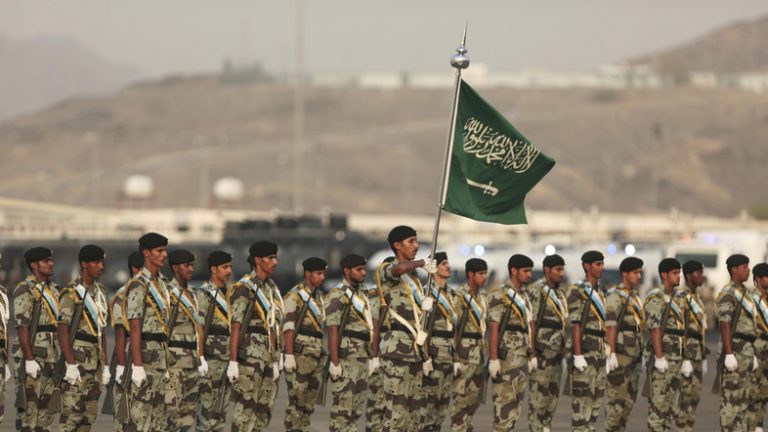
The military strategy of Saudi Arabia
Interview with
Dr. Hossein Rabiee
Expert in Strategic issues
In 1923, at the same time as the establishment of the Saudi state government, its military force, including the Saudi Army, was formed. After the discovery of oil and the meeting between King Abdul Aziz and President Franklin Roosevelt, the United States became the main ally of Saudi Arabia. The Arab-Israeli conflict in 1948, the fall of Mohammad Reza Pahlavi, the Shah of Iran and the fear of spreading Shi’ism, were among other factors contributing to the expansion of the Saudi Arabian army. According to data released by the CIA and the US Congressional Library in 2011, Saudi Arabia is ranked 26th in the world’s military power. Now, with regard to the war in Yemen and … the question is: How much is Saudi Arabia’s military power? To further explore this potential and military plans and goals of this country, we have discussed with Mr. Rabiee a defense and strategic adviser:
IIWFS: Can we say that Saudi Arabia’s military and defense strategies have changed dramatically over the past decade?
Since its independence in military and defense affairs, Saudi Arabia has become known in the region with two characteristics. On the one hand, Saudi Arabia has had a conservative and cautious policy among Middle Eastern countries and rarely entered military conflicts. On the other hand, it is always one of the most important buyers of military weapons in the world and has stored a large volume of military equipment in its warehouses. But in recent years, this country has been directly involved in the region’s military conflicts; it has supported militant groups in the region; its military force has entered Bahrain and has been fighting Yemen for more than two years. Therefore, Saudi Arabia clearly has set off an aggressive strategy in its foreign policy agenda, and the nature of its defense and military strategy seems to have changed dramatically.
IIWFS: How do you assess Saudi Arabia’s military status in the region and in the world?
In the Global Fire rankings and other ranking institutions, Saudi Arabia ranks 24-26 in the world and in the region is in the fourth or fifth category. Of course, I believe that ratings that are necessarily relying on figures are misleading because the warrior’s morale, intelligence and the power of decision-making or the proper response to warfare and such features, which are not in the figures, are crucial in military capabilities of countries and evidences show that the Saudi military faces fundamental problems in this regard. In the wars between Israel and the Arabs, this proved to be true and in the Six-Day Arab-Israeli War, the forces of several Arab countries suffered from a massive defeat of Israel. Therefore, relying on statistics and figures cannot show anything. Meanwhile, with Saudi Arabia’s annual and billionth purchases, it has a high ranking among the world’s armies.
IIWFS: According to some reports, the Saudi Air Force is considered the third military air power in the Middle East after the air force of Israel and Egypt. In the meantime, has the Saudi Arabian Air Force turned from a defensive force into an aggressive force with massive military purchases and the use of modern equipment? How has this affected the military capability and deterrence of this country in the region?
The experience of Saudi military operations against Yemen indicates that Saudi Arabia’s military and aggressive capabilities cannot be considered remarkably practical. It is worth noting that even these operations are apparently carried out in cooperation with several Arab countries and the use of forces outside of these countries; and so far, it has not succeeded in surrendering Ansarullah or achieving Saudi Arabia’s goals. The deterrence of this country has not changed much; because small countries such as Qatar and Oman did not succumb to Saudi demands and did not care about possible Saudi actions.
IIWFS: What is Saudi Arabia’s indigenous and industrial power in the field of military industries and its exports?
Saudi Arabia does not have a military manufacturing industry and news reports of arms trading in the world show that Saudi Arabia is a weapon importer from all producing countries and has not exported any weapons to other countries.
IIWFS: What components do you think military cooperation and its partnership with the United States can be measured in the past two years, with regard to the Persian Gulf missile system in Saudi Arabia?
Although military cooperation between the United States and Saudi Arabia has a long history, after the arrival of Donald Trump, this cooperation has increased and during his visit to Saudi Arabia, unprecedented contracts for the sale of military equipment to Saudi Arabia have been signed. According to some analysts, in recent months, Saudi cooperation with Israel has increased. Therefore, its cooperation with the United States is defined in the context of the unification of the United States with Israel. On the other hand, Saudi Arabia has shown enormous hostility to Iran over the past two years. Therefore, the US-Saudi alliance can be against the interests of Iran. Saudi Arabia is also intrigued by crises and issues that may cause unrest and, by approaching the United States, it wants to crack down on possible unrest. Therefore, Israel and the region, Iran and domestic issues are the main components of Saudi-US relations.
IIWFS: What is Saudi Arabia’s military role and potential in any possible attack on Iran?
Saudi Arabia has been purchasing and storing significant air defense equipment. But it needs to know that, as one US official had said a while ago, there would be no chance at all in any possible conflict to take out equipment from the warehouse. Of course, Saudi Arabia is also likely to be aware of its limited capabilities, and it is not unreasonable to always seek to create a coalition and unity with its associated countries.
IIWFS: What is the future of the country’s main military and defense strategies at the national and international level?
Part of Saudi defense and defense strategy is about regional issues. The Middle East is undergoing a transition and, as it is already unstable, it is anticipated that these unrest will not end soon. And of course, part of the reason for these unrest is back to the wrong policies of Saudi Arabia. Saudi Arabia is likely to continue its unattainable ambitions and will create further instability in the Middle East.
** This article is originally published in Persian and translated by A.R. Mirjomehri.